Chronic Pain - Nursing Care Plan for Chronic Pericarditis
Nursing Care Plan for Chronic Pericarditis
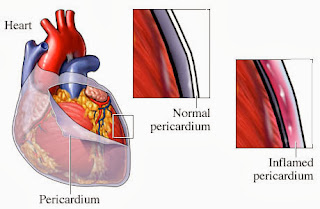
Pericarditis is the inflammation of the pericardium. It is caused by infection of the pericardium which is the thin, tough bag-like membrane surrounding the heart. The pericardium also prevents the heart from over expanding when blood volume increases. Symptoms of pericarditis include chest pain, mild fever, weakness, fatigue, coughing, hiccups, and muscle aches.
Pericarditis is the inflammation of the pericardium. It is caused by infection of the pericardium which is the thin, tough bag-like membrane surrounding the heart. The pericardium also prevents the heart from over expanding when blood volume increases. Symptoms of pericarditis include chest pain, mild fever, weakness, fatigue, coughing, hiccups, and muscle aches.
Chronic pericarditis is long-lasting, gradual inflammation of the pericardium, causing accumulation of fluid in the pericardial space or thickening of the pericardium. The chronic varieties of pericarditis are rare. Chronic pericarditis is usually be preceded by acute pericarditis (although acute pericarditis is more common and usually self-limiting).
Nursing Diagnosis and Interventions for Chronic Pericarditis
Chronic Pain related to inflammation of the pericardium
Interventions :
Rational :
Pericarditis is the inflammation of the pericardium. It is caused by infection of the pericardium which is the thin, tough bag-like membrane surrounding the heart. The pericardium also prevents the heart from over expanding when blood volume increases. Symptoms of pericarditis include chest pain, mild fever, weakness, fatigue, coughing, hiccups, and muscle aches.
Pericarditis is the inflammation of the pericardium. It is caused by infection of the pericardium which is the thin, tough bag-like membrane surrounding the heart. The pericardium also prevents the heart from over expanding when blood volume increases. Symptoms of pericarditis include chest pain, mild fever, weakness, fatigue, coughing, hiccups, and muscle aches.
Chronic pericarditis is long-lasting, gradual inflammation of the pericardium, causing accumulation of fluid in the pericardial space or thickening of the pericardium. The chronic varieties of pericarditis are rare. Chronic pericarditis is usually be preceded by acute pericarditis (although acute pericarditis is more common and usually self-limiting).
Nursing Diagnosis and Interventions for Chronic Pericarditis
Chronic Pain related to inflammation of the pericardium
Interventions :
- Investigate complaints of chest pain, note the onset and ballast factor or lowering. Pay attention to nonverbal cues of discomfort ; lay silent / anxiety, muscle tension, crying.
- Provide a quiet environment and comfort measures ; positional changes, emotional support.
- Give proper entertainment activities.
- Give medications as indicated.
- Provide supplemental oxygen as indicated.
Rational :
- Pain is typically located sublateral pericarditis and can spread to the neck and back. At this pain became worse in the deep inspiration, movement or lying down, and lost by sitting upright / bent.
- This action can reduce the patient's physical and emotional discomfort.
- Redirect attention, provide a distraction in the individual activity level.
- Can relieve pain, decrease the inflammatory response.
- To reduce fever and increase comfort.
- Maximizing the availability of oxygen for uptake to decrease the workload of the heart and lowers with respect to ischemic discomfort.

Comments
Post a Comment