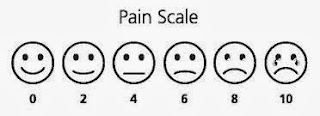
Examples of Pain Scales
A pain scale measures a patient's pain intensity or other features. Pain scales are based on self-report, observational (behavioral), or physiological data. Self-report is considered primary and should be obtained if possible (since pain is a quale by definition, and therefore assessment based on any set scale of expected outcomes from similar cases can fail to provide useful clinical data). Pain scales are available for neonates, infants, children, adolescents, adults, seniors, and persons whose communication is impaired. Pain assessments are often regarded as "the 5th Vital Sign." Examples of Pain Scales Infant Observational : Premature Infant Pain Profile; Neonatal/Infant Pain Scale Child Self-report : Faces Pain Scale - Revised; Wong-Baker FACES Pain Rating Scale; Coloured Analogue Scale Observational : FLACC (Face Legs Arms Cry Consolability Scale); CHEOPS (Children's Hospital of Eastern Ontario Pain Scale) Physiological : Comfort Adult Sel...