Acute Pain - Nursing Care Plan for Tonsillitis
Acute tonsillitis is an acute inflammation caused by Beta-Hemolytic Streptococcal, Viridans streptococci and Streptococcus pyogenes, can also be caused by a virus.
Etiology of Tonsillitis
1. Beta-Hemolytic Streptococcal
Beta-Hemolytic Streptococcal is a gram-positive bacterium that can multiply in a healthy throat and can cause acute respiratory tract infections.
2. Streptococcus pyogenes
Streptococcus pyogenes is a gram-positive bacterium that grows in a circular form long chains and lead group A streptococcal infection
Streptococcus pyogenes is the cause of many important human diseases ranging from infection typically begins in the throat and skin.
3. Viridans streptococci
Viridans streptococci has the unique ability dextran synthesis of glucose which allows them adhere to fibrin-platelet aggregates in damaged heart valves.
4. Influenza virus
The influenza virus is an RNA virus of the family Orthomyxo Viridae (influenza virus). The virus is transmitted by the medium of air, by sneezing in humans, common symptoms that occur are fever, sore throat, headache, nasal congestion. In a bad case of influenza can also cause pneumonia.
Classification of Tonsillitis
1. Acute tonsillitis
Acute tonsillitis caused by streptococcus on hemoliticus, viridians streptococcus, and Streptococcus pyogene, can also be caused by a virus.
2. Follicular tonsillitis
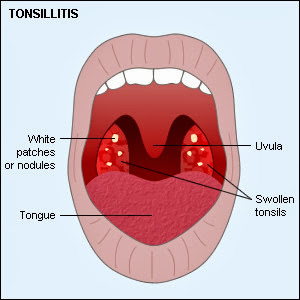
Tonsils swollen and hyperemic, covered its surface covered with patches of white exudate filling detritus called tonsil crypt. This detritus contained leukocytes, epithelial apart due to inflammation and the remnants of food stuck.
3. Lacunar Tonsillitis
Adjacent patches together and fill Lacuna (curves) surface of the tonsils.
4. Membranous Tonsillitis (Septic Sore Throat)
Tonsillar exudate covering the surface of the swollen membrane resembles. These membranes are usually easily removed or discarded and yellowish white.
5. Chronic Tonsillitis
Recurrent tonsillitis, predisposing factors: chronic stimulation (cigarettes, food) the effects of weather, the treatment of acute inflammation of inadequate and poor oral hygiene.
Nursing Diagnosis for Tonsillitis : Acute Pain Acute pain related to swelling of the tonsils
Goal : Pain ilang or reduced
Outcomes:
1. Assess complaints of pain, note the location, intensity (scale of 1-10), frequency and time. Marking non-verbal, eg restlessness, tachycardia, grimacing.
R:/ Indicate the need for intervention and also the signs of progression / resolution of complications.
2. Encourage expression of feelings.
R:/ Can reduce the anxiety and fear, thereby reducing the perception of the intensity of fear.
3. Provide entertainment activities, eg reading, watching TV, playing mobile phone.
R:/ Improve ability to cope with the attention back.
4. Perform palliative measures, eg changing positions, massage.
R:/ Increase relaxation / tension decreases.
5. Instruct patients to use visualization / guided imagery, progressive relaxation, deep breathing techniques.
R:/ Increase relaxation and feeling healthier.
6. Give analgesic / antipyretic. Use patient -controlled analgesia, to provide 24- hour analgesic doses.
R:/ R :/ Providing a decrease in pain or discomfort : reduce fever. Controlled drugs by patients or 24 hours of analgesia maintain blood levels remain stable. Prevent deficiency or excess drugs.
Etiology of Tonsillitis
1. Beta-Hemolytic Streptococcal
Beta-Hemolytic Streptococcal is a gram-positive bacterium that can multiply in a healthy throat and can cause acute respiratory tract infections.
2. Streptococcus pyogenes
Streptococcus pyogenes is a gram-positive bacterium that grows in a circular form long chains and lead group A streptococcal infection
Streptococcus pyogenes is the cause of many important human diseases ranging from infection typically begins in the throat and skin.
3. Viridans streptococci
Viridans streptococci has the unique ability dextran synthesis of glucose which allows them adhere to fibrin-platelet aggregates in damaged heart valves.
4. Influenza virus
The influenza virus is an RNA virus of the family Orthomyxo Viridae (influenza virus). The virus is transmitted by the medium of air, by sneezing in humans, common symptoms that occur are fever, sore throat, headache, nasal congestion. In a bad case of influenza can also cause pneumonia.
Classification of Tonsillitis
1. Acute tonsillitis
Acute tonsillitis caused by streptococcus on hemoliticus, viridians streptococcus, and Streptococcus pyogene, can also be caused by a virus.
2. Follicular tonsillitis
Tonsils swollen and hyperemic, covered its surface covered with patches of white exudate filling detritus called tonsil crypt. This detritus contained leukocytes, epithelial apart due to inflammation and the remnants of food stuck.
3. Lacunar Tonsillitis
Adjacent patches together and fill Lacuna (curves) surface of the tonsils.
4. Membranous Tonsillitis (Septic Sore Throat)
Tonsillar exudate covering the surface of the swollen membrane resembles. These membranes are usually easily removed or discarded and yellowish white.
5. Chronic Tonsillitis
Recurrent tonsillitis, predisposing factors: chronic stimulation (cigarettes, food) the effects of weather, the treatment of acute inflammation of inadequate and poor oral hygiene.
Nursing Diagnosis for Tonsillitis : Acute Pain Acute pain related to swelling of the tonsils
Goal : Pain ilang or reduced
Outcomes:
- Getting to know the causes.
- Recognize the onset of pain.
- Analgesic non -aid measures.
- Recognizing the symptoms of pain.
- Indicate the position / relaxed facial expression.
1. Assess complaints of pain, note the location, intensity (scale of 1-10), frequency and time. Marking non-verbal, eg restlessness, tachycardia, grimacing.
R:/ Indicate the need for intervention and also the signs of progression / resolution of complications.
2. Encourage expression of feelings.
R:/ Can reduce the anxiety and fear, thereby reducing the perception of the intensity of fear.
3. Provide entertainment activities, eg reading, watching TV, playing mobile phone.
R:/ Improve ability to cope with the attention back.
4. Perform palliative measures, eg changing positions, massage.
R:/ Increase relaxation / tension decreases.
5. Instruct patients to use visualization / guided imagery, progressive relaxation, deep breathing techniques.
R:/ Increase relaxation and feeling healthier.
6. Give analgesic / antipyretic. Use patient -controlled analgesia, to provide 24- hour analgesic doses.
R:/ R :/ Providing a decrease in pain or discomfort : reduce fever. Controlled drugs by patients or 24 hours of analgesia maintain blood levels remain stable. Prevent deficiency or excess drugs.

Comments
Post a Comment